Cervical cancer
Disease Description
Cervical cancer (CC) is one of the most common oncological diseases among women worldwide. Almost all cases of cancer are associated with HPV (human papillomavirus) infection, which is sexually transmitted.
According to World Health Organization statistics, every second case of cervical cancer subsequently becomes the cause of death. Almost one-third of patients visit a doctor with advanced stages of oncology.
Symptoms indicating the need to seek diagnosis and treatment
In the early stages, cervical cancer is asymptomatic. The appearance of symptoms indicates the progression of the malignant process and the involvement of adjacent organs and lymph nodes.
The most prominent clinical manifestations of CC are:
- Bleeding: intermenstrual, contact (after sexual intercourse), postmenopausal
- Heavy menstruation
- Vaginal discharge: yellowish, profuse watery
- Pelvic pain: radiating to the coccyx, pubic symphysis
Diagnosis and treatment methods
Diagnosis
Cervical cancer can be suspected during speculum examination, colposcopy, and based on the results of cytological analysis.
Diagnosis of cervical cancer in European clinics is based on histology results, with material obtained during targeted or scalpel biopsy. Additionally, patients are prescribed an SCC tumor marker test (squamous cell carcinoma antigen).
Treatment
The main method of treatment is surgical. Physicians in leading clinics worldwide focus on organ-preserving surgeries (especially for patients of reproductive age). Sometimes chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy are added to the primary treatment.
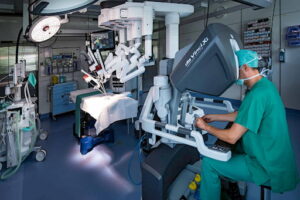
As an advanced surgical method, the Da Vinci robot is used, which reduces the duration of surgery and increases its precision several times over. In top clinics, the latest-generation robotic assistant, featuring an improved position of manipulators and 3D imaging, helps to combat cervical cancer.
Innovations of world clinics
For the treatment of inoperable cancer, specialists in top clinics use a unique method of isolated chemoperfusion. The essence of the method is to convert the tumor from an unresectable state to a removable one, after which surgical treatment is carried out. As a result, the patient has a chance to get rid of the tumor permanently and avoid recurrences in the future.